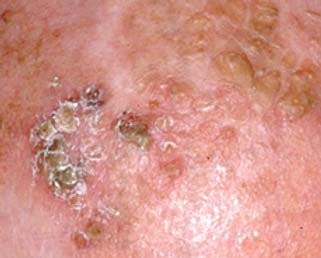
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common type of skin cancer.
In general is rare for SCC to spread to other parts of the body (metastasize). It is mostly found on areas of the skin with most sun exposure (head, neck, hands, forearms, and lower legs)
It generally grows faster than BCC (Basal Cell Carcinoma).
Squamous cell carcinoma symptoms:
- Red irritated spot
- Scaly
- rapidly growing
- non healing sore
- may develop in old scars
- may be tender to touch.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) treatment:
Treatment of SCC depends on many factors, to simplify we have these factors that suggest a high-risk SCC.
SCC on lip or ear
Size:
- ≥2 cm on the trunk or extremities (excluding pretibia, hands, feet, nail units, and ankles)
- ≥1 cm on the cheeks, forehead, scalp, neck, or overlying the shin
- ≥0.6 cm on the “mask” areas of the face (central face, eyelids, eyebrows, periorbital skin, nose, cutaneous or vermillion lip, chin, mandible, preauricular and postauricular skin, temple, and ear), genitalia, hands, and feet.
SCC that has grown from a scar or long term wound
Nerve symptoms (weakness, tingling or numbness) that may indicate nerve involvement.
Features at the lab after a biopsy has been sent that may suggest more dangerous cancer (Tumors with poorly differentiated histology, deep microinvasion, or perineural invasion are more likely to behave aggressively.)
For low risk lesions a variety of treatment options are possible.
For low risk SCC-in-situ (Bowen’s disease) I prefer to use efudix (5-fluoruracil), a cream we apply to the area twice a day for 4 – 8 weeks depending on treatment response.
Other options include surgical removal, cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen), imiquimod cream, radiation therapy and photodynamic therapy. In general I prefer efudix or surgical removal because they have the greatest cure rate with least complication.